The pancreas might not be the star of the show when it comes to human anatomy, but this unsung hero plays a crucial role in keeping the body running smoothly. Nestled snugly between the stomach and the spine, it’s like that reliable friend who always shows up when you need them—just without the fanfare. So, what system does this multitasking organ belong to? Spoiler alert: it’s not just hanging out by itself.
This powerhouse is a key player in both the digestive and endocrine systems. While it whips up enzymes to help break down food, it also releases hormones like insulin to keep blood sugar levels in check. If the pancreas were a superhero, it’d be the one juggling multiple responsibilities while still managing to save the day—albeit without a cape. Understanding its role can help demystify how the body operates and why keeping this organ healthy is essential.
Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding the Pancreas
The pancreas plays a crucial role in human anatomy, bridging the digestive and endocrine systems. Its location between the stomach and spine enhances its significance in various bodily functions.
Anatomy of the Pancreas
This organ is elongated and shaped like a fish, measuring about six to eight inches long. The pancreas consists of three main sections: the head, body, and tail. The head lies nestled in the curve of the duodenum, while the body extends across the abdomen, ending at the tail. Surrounding tissues, particularly the spleen and stomach, help protect it. Blood vessels and nerves provide essential connectivity to other organs.
Functions of the Pancreas
The pancreas serves dual purposes, contributing to digestion and hormone regulation. Digestive enzymes it produces, such as amylase and lipase, aid in breaking down carbohydrates and fats. Insulin and glucagon, two critical hormones, maintain blood sugar levels. When food enters the small intestine, pancreatic enzymes activate, helping nutrient absorption. Hormonal secretions respond to blood glucose changes, ensuring energy balance.
The Endocrine System
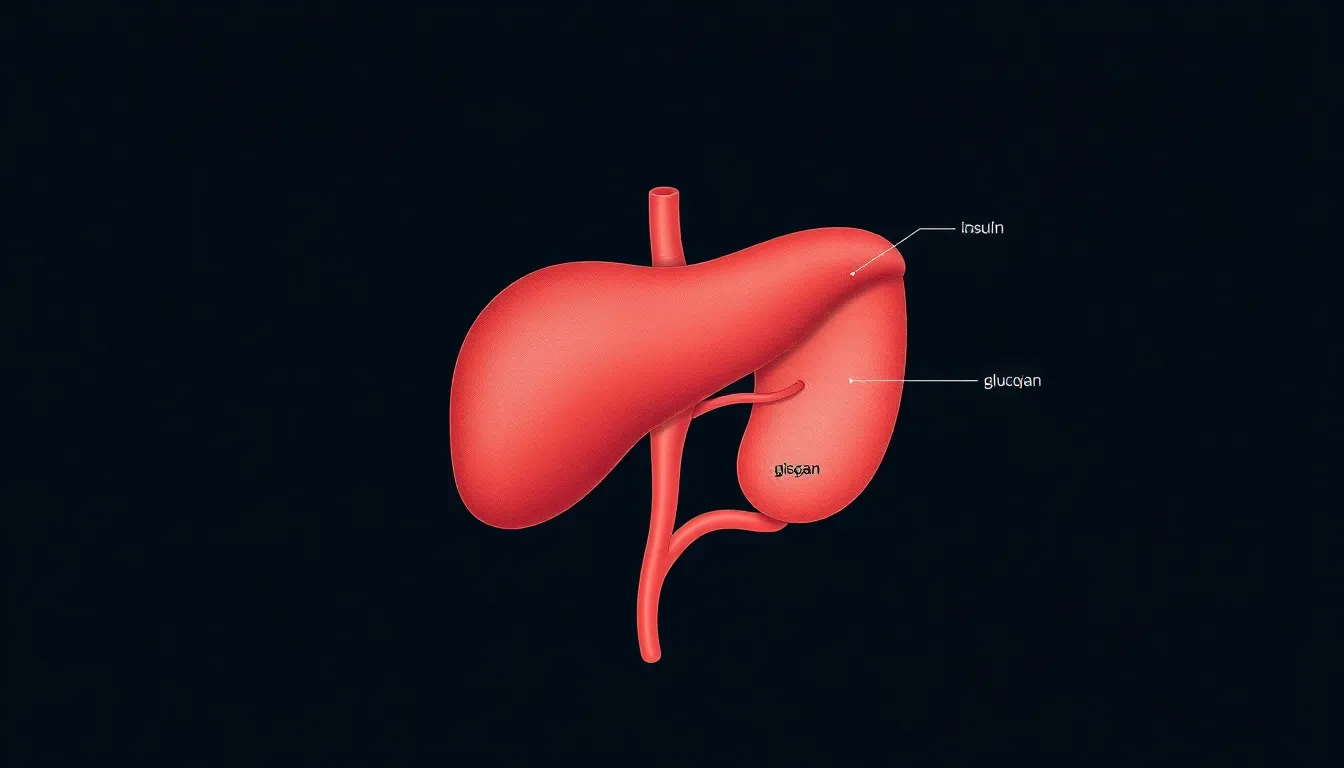
The pancreas plays a vital role in the endocrine system, regulating several critical body functions. This organ helps manage blood sugar levels through hormone production.
Role of the Pancreas in the Endocrine System
In the endocrine system, the pancreas produces hormones that control glucose metabolism. Insulin and glucagon, produced by the pancreas, work together to maintain glucose homeostasis. Insulin lowers blood sugar, facilitating cellular uptake. Glucagon raises blood sugar by signaling the liver to release stored glucose. The balance between these two hormones is essential for energy regulation and overall metabolic health.
Hormones Produced by the Pancreas
The pancreas produces several important hormones. Insulin lowers blood sugar levels, while glucagon raises them. Somatostatin, another hormone, inhibits hormone secretion to maintain balance. Pancreatic polypeptide assists in digestion by regulating pancreatic secretions. Each hormone fulfills a specific function, contributing to the body’s metabolic processes and energy management.
The Digestive System
The pancreas plays a crucial role in digestion. Positioned between the stomach and spine, it produces essential enzymes that aid in breaking down food. Enzymes work in the small intestine, facilitating the absorption of nutrients. This organ’s functionality ensures the body processes carbohydrates, proteins, and fats efficiently.
Function of the Pancreas in Digestion
The pancreas contributes significantly to digestive health. It releases digestive juices into the small intestine, essential for food breakdown. Nutrient absorption becomes possible through these juices, specifically targeting fats, proteins, and carbohydrates. Maintaining robust digestive function relies heavily on the pancreas’s effectiveness.
Enzymes Secreting from the Pancreas
Numerous enzymes secreted by the pancreas support digestion. Amylase, for instance, breaks down carbohydrates into simpler sugars. Lipase specifically targets fats, enabling their absorption. Proteases like trypsin and chymotrypsin digest proteins into amino acids. Each enzyme plays a distinctive role, ensuring that digestion occurs seamlessly and efficiently.
Connection Between Systems
The pancreas plays a vital role in the interplay between the endocrine and digestive systems. It produces hormones like insulin and glucagon that regulate blood sugar levels and also secretes digestive enzymes essential for macronutrient breakdown. Enzymes such as amylase, lipase, and proteases directly contribute to digestion while hormone production influences metabolism. The synthesis of these hormones and enzymes exemplifies synergy between the two systems, showcasing how one affects the functions of the other.
How the Endocrine and Digestive Systems Interact
The endocrine system regulates numerous body functions through hormones, while the digestive system breaks down food for nutrient absorption. When food enters the intestines, the pancreas releases enzymes that facilitate this process. Simultaneously, it releases hormones such as insulin, crucial for managing glucose from digested carbohydrates. Insulin directs glucose into cells for energy. Glucagon, on the other hand, acts when blood sugar levels drop, prompting the liver to release stored glucose. This interaction ensures energy availability and nutrient utilization, emphasizing the pancreas’s central role.
Impact of Pancreatic Health on Overall Wellbeing
Maintaining pancreatic health directly influences overall wellbeing. Disorders like diabetes stem from pancreatic dysfunction, leading to impaired insulin secretion. This can cause significant fluctuations in blood sugar levels, affecting energy and mood. Additionally, pancreatic issues may hinder digestive enzyme production, resulting in malabsorption of nutrients. Nurturing pancreatic health through a balanced diet and regular exercise supports efficient digestion and hormone regulation. Prioritizing this organ’s well-being promotes overall metabolic health and enhances quality of life.
The pancreas plays a pivotal role in maintaining both digestive and endocrine health. By producing essential enzymes and hormones it ensures proper nutrient absorption and blood sugar regulation. Understanding its functions highlights the need for awareness regarding pancreatic health.
Maintaining a balanced diet and staying active can support this vital organ’s performance. Awareness of the pancreas’s dual functions can empower individuals to take proactive steps in promoting their overall well-being. Prioritizing pancreatic health is crucial for achieving optimal metabolic function and enhancing quality of life.



